BepiColombo Spies Escaping Oxygen and Carbon in Unexplored Region of Venus’s Magnetosphere
A fleeting visit of the ESA/JAXA BepiColombo mission to Venus has revealed surprising insights into how gases are stripped away from the upper layers of the planet’s atmosphere.
Detections in a previously unexplored region of Venus’s magnetic environment show that carbon and oxygen are being accelerated to speeds where they can escape the planet’s gravitational pull. The results have been published today in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Lina Hadid, CNRS researcher at the Plasma Physics Laboratory (LPP) and lead author of the study said: “This is the first time that positively charged carbon ions have been observed escaping from Venus’s atmosphere. These are heavy ions that are usually slow moving, so we are still trying to understand the mechanisms that are at play. It may be that an electrostatic ‘wind’ is lifting them away from the planet, or they could be accelerated through centrifugal processes.”
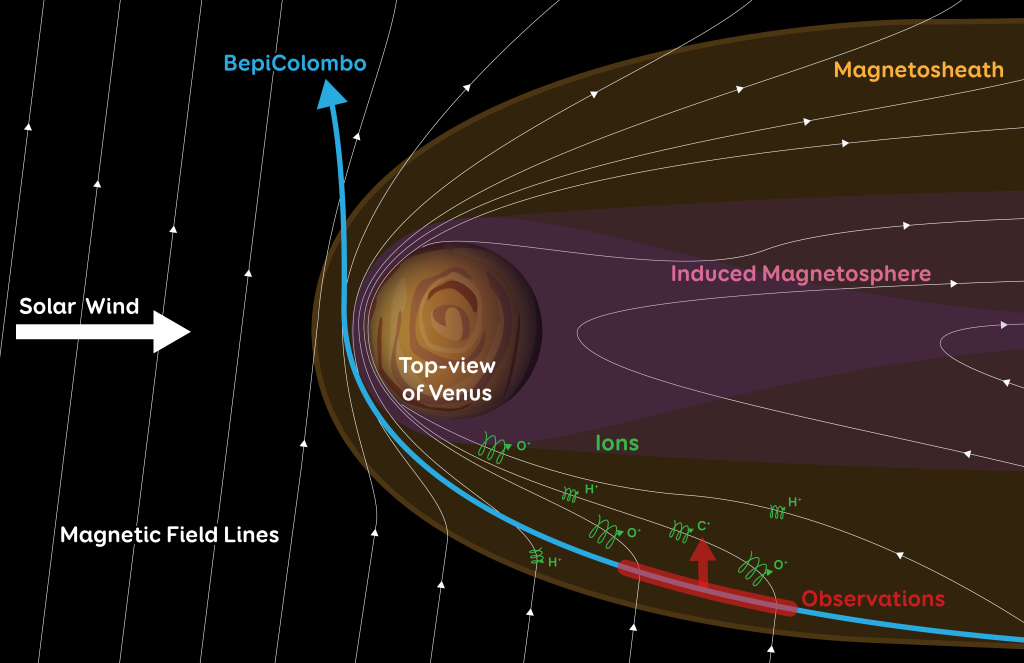
Unlike Earth, Venus does not generate an intrinsic magnetic field in its core. Nonetheless, a weak, comet-shaped ‘induced magnetosphere’ is created around the planet by the interaction of charged particles emitted by Sun (the solar wind) with electrically charged particles in Venus’s upper atmosphere. Draped around the magnetosphere is a region called the ‘magnetosheath’ where the solar wind is slowed and heated.
On 10 August 2021, BepiColombo passed by Venus to slow down and adjust course towards its final destination of Mercury. The spacecraft swooped up the long tail of Venus’s magnetosheath and emerged through the nose of the magnetic regions closest to the Sun. Over a 90-minute period of observations, BepiColombo’s instruments measured the number and mass of charged particles it encountered, capturing information about the chemical and physical processes driving atmospheric escape in the flank of the magnetosheath.
Early in its history, Venus had many similarities to Earth, including significant amounts of liquid water. Interactions with the solar wind have stripped away the water, leaving an atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide and smaller amounts of nitrogen and other trace species. Previous missions, including NASA’s Pioneer Venus Orbiter and ESA’s Venus Express have made detailed studies of the type and quantity of molecules and charged particles that are lost into space. However, the missions’ orbital paths left some areas around Venus unexplored and many questions still unanswered.
Data for the study were obtained by BepiColombo’s Mass Spectrum Analyzer (MSA) and the Mercury Ion Analyzer (MIA) during the spacecraft’s second Venus flyby. The two sensors are part of the Mercury Plasma Particle Experiment (MPPE) instrument package, which is carried by Mio, the JAXA-led Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter.
“Characterising the loss of heavy ions and understanding the escape mechanisms at Venus is crucial to understand how the planet’s atmosphere has evolved and how it has lost all its water,” said Dominique Delcourt, researcher at LPP and the Principal Investigator of the MSA instrument.
Europlanet’s SPIDER space weather modelling tools enabled the researchers to track how the particles propagated through the Venusian magnetosheath.
“This result shows the unique results that can come out of measurements made during planetary flybys, where the spacecraft may move through regions generally unreachable by orbiting spacecraft,” said Nicolas André, of the Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (IRAP) and lead of the SPIDER service.
A fleet of spacecraft will investigate Venus over the next decade, including ESA’s Envision mission, NASA’s VERITAS orbiter and DAVINCI probe, and India’s Shukrayaan orbiter. Collectively, these spacecraft will provide a comprehensive picture of the Venusian environment, from the magnetosheath, down through the atmosphere to the surface and interior.
“Recent results suggest that the atmospheric escape from Venus cannot fully explain the loss of its historical water content. This study is an important step to uncover the truth about the historical evolution of the Venusian atmosphere, and upcoming missions will help fill in many gaps,” added co-author, Moa Persson of the Swedish Institute of Space Physics.
Publication details:
Hadid et al. BepiColombo observations of oxygen and carbon ions in the flank of Venus induced magnetosphere. Nature Astronomy, 12 April 2024.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41550-024-02247-2
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-024-02247-2
Images
Download image file as: JPG | PNG | PDF
Science Contacts
Dr Lina Hadid
Laboratoire de Physique des Plasmas (LPP)
Palaiseau
France
lina.hadid@lpp.polytechnique.fr
Dr Dominique Delcourt
Laboratoire de Physique des Plasmas (LPP)
Palaiseau
France
dominique.delcourt@lpp.polytechnique.fr
Dr Moa Persson
Institutet för Rymdfysik (IRF)
Swedish Institute of Space Physics
Uppsala
Sweden
moa.persson@irf.se
Dr Nicolas André
Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (IRAP)
Toulouse
France
Nicolas.andre@irap.omp.eu
Media Contacts
Anita Heward
Press Officer
Europlanet 2024 Research Infrastructure (RI)
+44 7756 034243
aheward@europlanet-society.org
Thibaut Roger
Press Officer
Europlanet 2024 Research Infrastructure (RI)
thibaut.roger@science-elegance.com
Further Information
About ISAS/JAXA
In October 2003, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) was established as an independent administrative institution, integrating the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) and the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL). ISAS became one of four principal sections within the newly established organization. Its mission is to advance space science – scientific research conducted in outer space – in Japan, mainly by collaboration with universities. It also actively contributes to JAXA’s and Japan’s entire space development.
ISAS’s new efforts and results in space science are published in Japan and shared with the international community, thus promoting JAXA’s status and enhancing Japan’s intellectual reputation in the world.
Web: https://www.isas.jaxa.jp/en/
Twitter: @ISAS_JAXA_EN
About Europlanet
Since 2005, Europlanet has provided Europe’s planetary science community with a platform to exchange ideas and personnel, share research tools, data and facilities, define key science goals for the future, and engage stakeholders, policy makers and European citizens with planetary science.
The Europlanet 2024 Research Infrastructure (RI) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 871149 to provide access to state-of-the-art research facilities and a mechanism to coordinate Europe’s planetary science community. The project builds on a €2 million Framework 6 Coordination Action (EuroPlaNet), a €6 million Framework 7 Research Infrastructure (Europlanet RI) and a €10 million Horizon 2020 Research Infrastructure (Europlanet 2020 RI) funded by the European Commission.
The Europlanet Society promotes the advancement of European planetary science and related fields for the benefit of the community and is open to individual and organisational members. The Society’s aims are:
- To expand and support a diverse and inclusive planetary community across Europe through the activities of its 10 Regional Hubs.
- To build the profile of the sector through outreach, education and policy activities
- To underpin the key role Europe plays in planetary science through developing links at a national and international level.
Europlanet 2024 RI project website: www.europlanet-2024-ri.eu
Europlanet Society website: www.europlanet-society.org
Follow on Twitter via @europlanetmedia

