ExoClock Counts Down Ariel Exoplanet Targets
Details of the orbits of 450 candidate exoplanet targets of the European Space Agency’s Ariel space mission have been presented this week at the Europlanet Science Congress (EPSC) 2022, and submitted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. The study, coordinated by the ExoClock (www.exoclock.space) project, has been co-authored by 217 professional and amateur astronomers, as well as university and high school students.
“The ethos of ExoClock can be described in three key words: inclusive, interactive, and integrated. It is open to everyone and accepts contributions from amateur astronomers, students, schools and public citizens,” said Anastasia Kokori, ExoClock project coordinator. “This is the third paper produced by the ExoClock team. The majority of the authors are amateur observers – around 160 – and this significant number highlights the interest and the value of the amateur community in contributing to space research.”
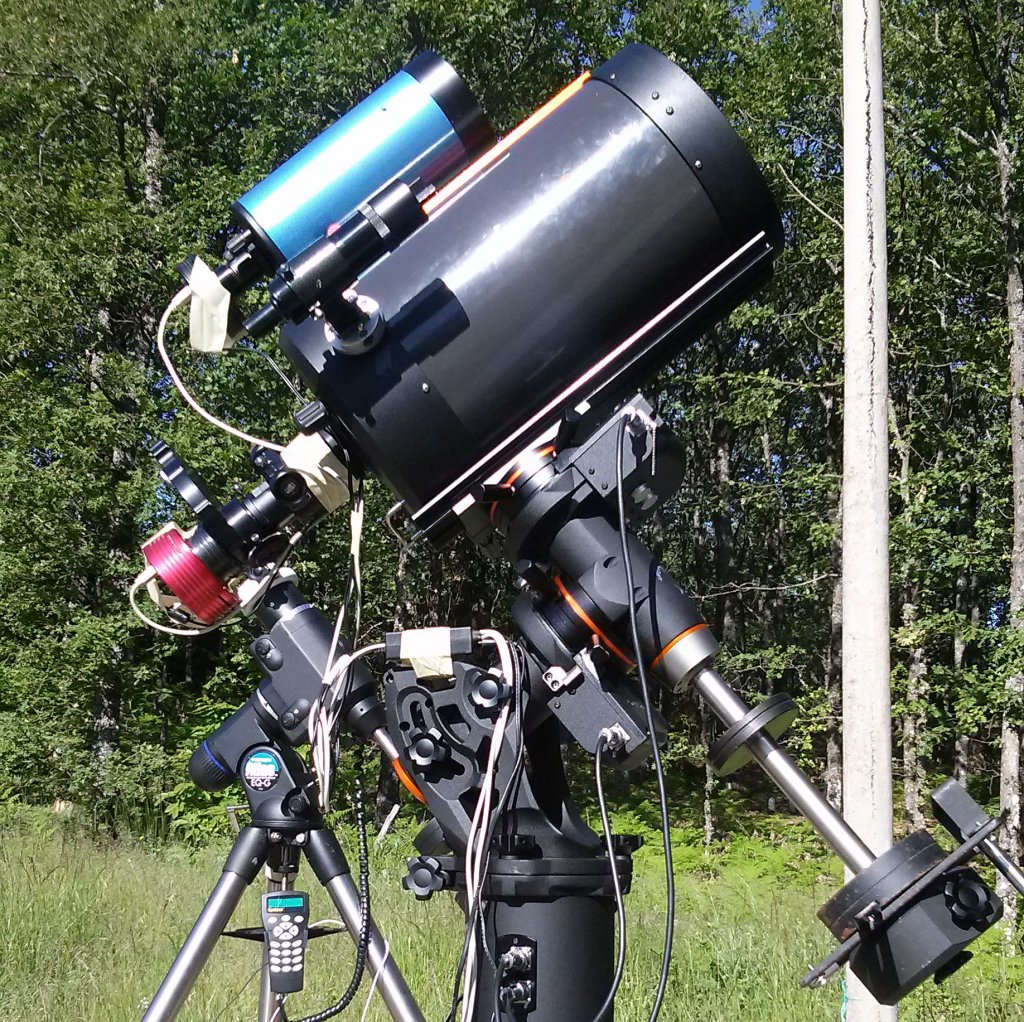
Ariel will study a population of more than 1000 exoplanets to characterise their atmospheres. The ExoClock project, which launched in September 2019, aims to support the long-term monitoring of exoplanets through regular observations using small and medium scale telescopes.
Participants submit measurements known as ‘light curves’, which show the drop in intensity as a planet ‘transits’ or passes in front of its host star and blocks some of the light. When Ariel launches in 2029, it will need to have precise knowledge of the expected transit time of each exoplanet that it observes, in order to maximise the mission’s efficiency and impact.
“The new study showed that over 40% of ephemerides for proposed Ariel targets needed to be updated. This highlights the important role that the ExoClock community can play in monitoring the Ariel targets frequently,” said Tsiaras.
ExoClock participants schedule and carry out observations, analyse the data and submit their results for review and feedback from members of the science team. This interactive process helps maintain consistency in results, and enriches the experience of the participants who learn through dialogue.
The results show that small and medium sized telescopes can successfully observe ephemerides for the large majority of the Ariel candidate targets. They also show how observations by amateur astronomers using their own telescopes can contribute to real science and have a high impact for a mission. The project helps to integrate Ariel with other space missions, ground-based telescopes, literature data and wider society, making best use of all available resources.
Kokori said: “Science is for everyone, and we are very happy that through the project everyone can be part of a real space mission. Our observers come from more than 35 countries and have different backgrounds. It is wonderful to see so many people willing to learn and work together in a collaborative spirit. Our team keeps growing daily with participants from all over the world.”
Images
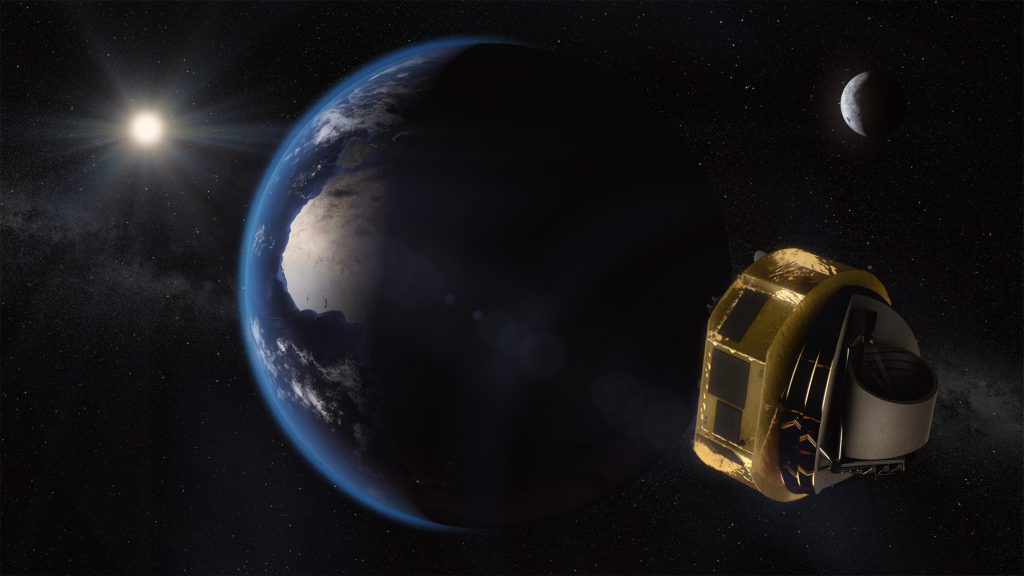
Artist’s impression of the Ariel mission.


Further information
The project is part of the Ariel ephemerides working group, aiming to refine the ephemerides of Ariel targets.
The updated ephemerides were produced as a result of a combination of around 18000 data points: 2911 observations from the ExoClock network, 12633 light curves from space telescopes, 2442 mid-time points from the literature and 184 observations provided by the Exoplanet Transit Database (ETD).
The pre-print of the publication is available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.09673
The database is accessible at OSF: https://osf.io/p298n/
Science Contacts
Anastasia Kokori
UCL
London, UK
anastasia.kokori.19@ucl.ac.uk
Angelos Tsiaras
Arcetri Astrophysical Observatory – INAF
Florence, Italy
angelos.tsiaras@inaf.it
MEDIA CONTACTS
EPSC2022 Press Office
+44 7756 034243
epsc-press@europlanet-society.org
FURTHER INFORMATION
About the Europlanet Science Congress (EPSC)
The Europlanet Science Congress (https://www.epsc2022.eu/) formerly the European Planetary Science Congress, is the annual meeting of the Europlanet Society. With a track record of 16 years, and regularly attracting around 1000 participants, EPSC is the largest planetary science meeting in Europe. It covers the entire range of planetary sciences with an extensive mix of talks, workshops and poster sessions, as well as providing a unique space for networking and exchanges of experiences.
Follow on Twitter via @europlanetmedia and using the hashtag #EPSC2022.
Details of media briefings and recordings can be found at: https://www.europlanet-society.org/press-briefings-at-epsc2022/
All Europlanet media releases can be found at: https://www.europlanet-society.org/press/
About Europlanet
Since 2005, Europlanet (www.europlanet-society.org) has provided Europe’s planetary science community with a platform to exchange ideas and personnel, share research tools, data and facilities, define key science goals for the future, and engage stakeholders, policy makers and European citizens with planetary science. In 2022, EPSC is held jointly with the European Astrobiology Network Association (EANA) annual meeting.
The Europlanet 2024 Research Infrastructure (RI) has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 871149 to provide access to state-of-the-art research facilities and a mechanism to coordinate Europe’s planetary science community.
The Europlanet Society promotes the advancement of European planetary science and related fields for the benefit of the community and is open to individual and organisational members. The Europlanet Society is the parent organisation of the Europlanet Science Congress (EPSC).
About EANA
The European Astrobiology Network Association (http://www.eana-net.eu), joins together people interested in the origins of life and the search for extraterrestrial life in the Solar System and beyond. This interdisciplinary domain involves scientists from multiple disciplines such as chemistry, physics, biology, geology, astronomy, and human sciences.



